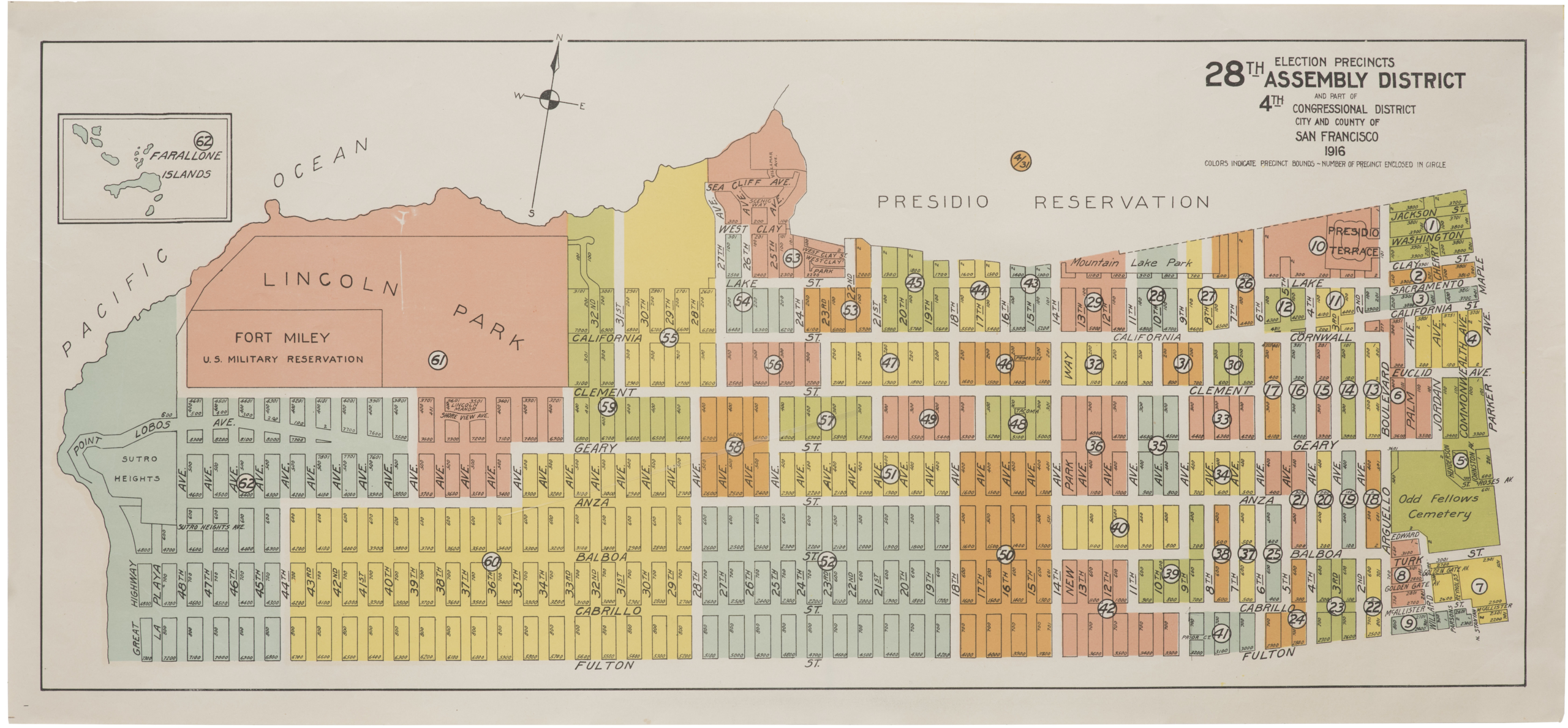
A rare circa 1912 cadastral plan of the nascent San Francisco neighborhood of St. Francis Wood.
St. Francis Wood: San Francisco’s Residence Park
Out of stock
Description
Rare real estate map of the housing development of St. Francis Wood, across Portola Avenue from the West Portal tunnel in San Francisco’s Sunset District. The map is oriented with north towards the left, and bounded by Yerba Buena Ave., St. Francis Park, Monterey Blvd., Junipero Serra Blvd., and Portola Drive. It shows block and lot numbers, lot sizes, and includes a small inset location map.
A history of St. Francis Wood
In the early years of this century, the area of San Francisco west of Twin Peaks remained largely undeveloped, awaiting an engineering breakthrough to allow easy access from the heavily populated sections to the north. That breakthrough came with the construction of the Twin Peaks trolley car tunnel. The planning for this tunnel began several years before its completion in 1917, and developers could foresee the potential it presented for residential subdivisions.
Mason-McDuffie was the first real estate company to take advantage of this opportunity, when it began planning a new residential park in 1912 along the western slope of Mt. Davidson. This new community was named St. Francis Wood, to emphasize the neighborhood’s planned harmony with its natural setting. In order to insure that the street plan for St. Francis Wood would strike a perfect balance with the preservation of large areas of open parkland, Duncan McDuffie hired the nationally renowned landscape architecture firm of Olmsted Brothers from Brookline, Massachusetts. The patriarch of this illustrious family, Frederick Law Olmsted, Sr., had been the creative force behind the landscape design of such famous public sites as Central Park in New York and Yosemite National Park.
The younger Olmsted Brothers were employed by Mason-McDuffie for several of their earlier developments, and they now put their energies into making St. Francis Wood one of the finest residential parks in the nation. In accordance with Duncan’s stipulations, all electric and telephone wires were placed underground, and St. Francis Park was created at the eastern end of St. Francis Boulevard. All the streets were laid out to conform to the tract’s natural topography. These plans were carefully integrated with the work of supervising architect John Galen Howard, who designed the graceful Beaux-Arts style entrance portals at the mouth of St. Francis Boulevard and the monumental fountain and terraced plaza at its terminus. From the upper steps of this plaza, residents and visitors can still observe a sweeping vista down the broad tree-lined boulevard to the Farallones on the Pacific horizon.
The outbreak of the first World War in 1914 occurred just as the first residential lots in St. Francis Wood were opened up for sale. For the next five years, the real estate market in San Francisco remained depressed, jeopardizing the survival of the entire project. In 1919, however, the market began to improve again, and construction in St. Francis Wood resumed at a healthy pace. Here, as for the Claremont Park development, firm restrictions on the type and quality of construction were strictly enforced. No “apartment houses, groceries, laundries, saloons, stables, or undertaking establishments” were allowed, and any balconies or overhanging extensions which blocked a neighbor’s view or sunlight were prohibited. Each home had to sit at least fifteen feet back from the sidewalk, and a minimum construction cost of $6,000 was mandated to guarantee a high caliber of house design.
After Howard stepped down as supervising architect, Henry Gutterson, a student and protege of Bernard Maybeck, succeeded him. Gutterson designed many of the finest homes in St. Francis Wood during his twenty-year tenure, as well as the circle fountain near the main entrance. By 1925, 500 families lived in St. Francis Wood, and it was being used as a model for residential parks as far away as Kansas City, where developer J.J. Nichols incorporated many of Mason-McDuffie’s ideas into his subdivisions. Its reputation was even known in Europe. Dr. Werner Hegemann, the top city planner in Germany, came to study St. Francis Wood and afterwards described it as “…the most distinguished residential suburb not alone in California, but in America.”
Census
OCLC/WorldCat lists only one copy of this version, at the California Historical Society; two larger versions are held at U.C. Berkeley and U.C. Davis.
Cartographer(s):
The Mason-McDuffie Company, founded in 1887 by Duncan McDuffie and Joseph Mason, was a prominent real estate firm based in California that significantly influenced urban development in the San Francisco Bay Area and beyond. The company played a key role in planning and developing iconic neighborhoods such as Claremont in Berkeley and Oakland, Northbrae in Berkeley, and St. Francis Wood in San Francisco. These neighborhoods were designed with an emphasis on high aesthetic standards, architectural harmony, and community planning, reflecting Mason-McDuffie’s pioneering approach to master-planned residential developments.
Condition Description
Old folds, with some wear along them and at edges; very good.
References
![[1906 EARTHQUAKE PANORAMA – FINANCIAL DISTRICT]](https://neatlinemaps.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Screen-Shot-2023-02-06-at-6.55.56-PM-300x300.png)