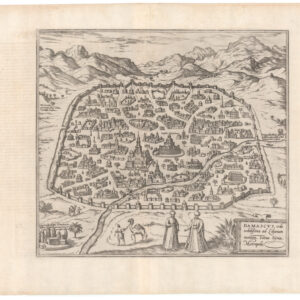
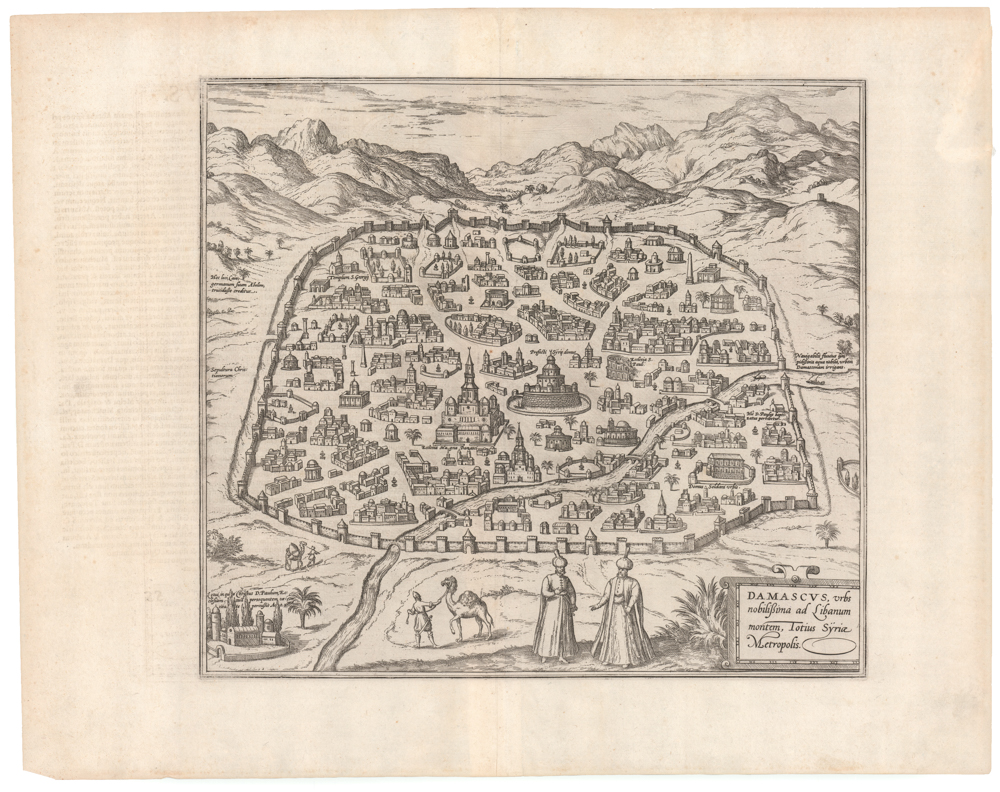
Lovely 19th-century view of al-Aqsa Mosque and surrounding countryside.
Western View of el-Aksa, near the South-Western Angle.
$320
1 in stock
Description
This plate provides a bird’s eye view of the iconic al-Aqsa mosque, located atop the Temple Mount in Jerusalem. This is the official mosque of the greater Haram al-Sharif complex, the third most holy site in Islam, and an important location in Christianity and Judaism as well. The Aqsa mosque dates back to the first century of Islam, founded around the turn of the 8th century CE. The view looks against the back- or qibla-wall, which directs Muslim prayer towards Mecca.
At the center of the complex, we see the domed and elevated central nave of the prayer hall, a characteristic trait of mosques from this period. The minaret was added later, presumably in the Ayyubid 13th century. Built against the outer wall of the mosque are the remains of a bridge that once provided private access to the mosque from the caliph’s three enormous palaces located immediately outside the Haram al-Sharif.
Pierotti’s view identifies a number of important elements in the landscape by means of a numbered legend that accompanies the lithograph:
1. Mount of Olives.
2. Mount Viri-Galilæi.
3. Mosque of the Ascension of Jesus Christ.
4. Arab Tower.
5. Mount of Offence.
6. Place where Jesus wept over Jerusalem.
7. Mosque el-Aksa.
8. Minaret of the Mogarabins.
9. Mosque of Abu-Bekr: Wall of the period of the Crusades.
Publication information
In 1864, the same year that the first British Ordnance Survey of Jerusalem was commissioned, Italian engineer Ermete Pierotti published Jerusalem Explored, a seminal work on the history, archaeology, and architectural history of the ancient and holy city. This work included Pierotti’s notes and insights after years of surveying and mapping under Ottoman authority. The publication was divided into a text volume and a volume of plates. The latter included 63 lithographs showing everything from strategic views, across architectural plans and section profiles, to panoramic vistas of the Old City. Most of the lithographed plates were based either on photographs or drawings made by Pierotti and his team.
The plates were lithographed mainly by Thomas Picken of London and printed by the prominent British lithography firm William Day & Sons.
Cartographer(s):
Ermete Pierotti (1820-1880) was the oldest of nine siblings in a family from Pontardeto in Pieve Fosciana (the family built the Palazzo Pierotti, which has served as the town hall since 1877). Pierotti worked as a military engineer in Genoa and later served as a captain in the Engineering Corps of the Sardinian King. In 1849, he was accused of desertion and the theft of 3596 lire from the troop’s treasury, which resulted in a dishonorable discharge from the army. Pierotti then traveled to Jerusalem and Egypt, where he worked as an engineer. In Egypt, he discovered the foundations of the Alexandria Library while laying the foundations for a Greek church, but it was in Jerusalem that he would put his surveying and engineering skills to work.
Pierotti arrived in Jerusalem in 1854 as a consultant for the Franciscan Order, which had custody of many of the Christian holy sites in the city. During his time there, Pierotti was involved in the restoration of the Crusader Era Church of St. Anne, located in the Old City near the Pool of Bethesda. Working with Ottoman engineer Assad Effendi, he later contributed to the restoration of the Qanat as-Sabil, the main aqueduct that supplied Jerusalem with water, which involved repairing the aqueduct’s channels and cisterns. Other building projects included work on the Temple Mount itself and the construction of both the Austrian Hospice and the so-called Alexanderhof (HQ of the Kaiserlichen Orthodoxen Palästina-Gesellschaft) in the Christian Quarter of the Old City. And finally, he helped design the road from Jaffa to Jerusalem, a significant engineering feat at the time.
Pierotti became interested in the city’s history and archeology during his time in Jerusalem. He conducted several excavations in the Old City. He discovered several important artifacts, including an inscription in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre that proved the existence of a church on the site during the Byzantine period. Pierotti’s work in Jerusalem earned him a reputation as a skilled engineer and pioneering archeologist. He became known for his attention to detail and ability to work under challenging conditions. In addition to his many projects, Pierotti’s legacy consists of publishing his magnum opus: Jerusalem Explored. A Description of the Ancient and Modern City (1864), which included an entire volume of lithographed plates based on Pierotti’s plans and converted photographs.
Despite his many successes, Pierotti’s work and position annoyed the British, who increasingly sought to establish a scientific presence in the Holy City, if not a colonial one. When competition arose between Pierotti and Captain Charles Wilson’s team of English Royal Engineers conducting the first Ordnance Survey of Jerusalem and surroundings in 1864, Pierotti’s reputation was deliberately tarnished by the disclosure of his criminal past, and for the rest of his life, he struggled to regain recognition for his achievements.
Condition Description
Excellent.
References