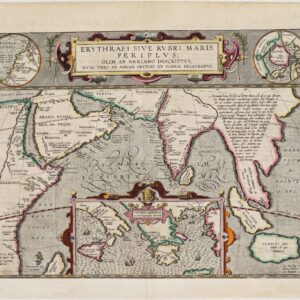
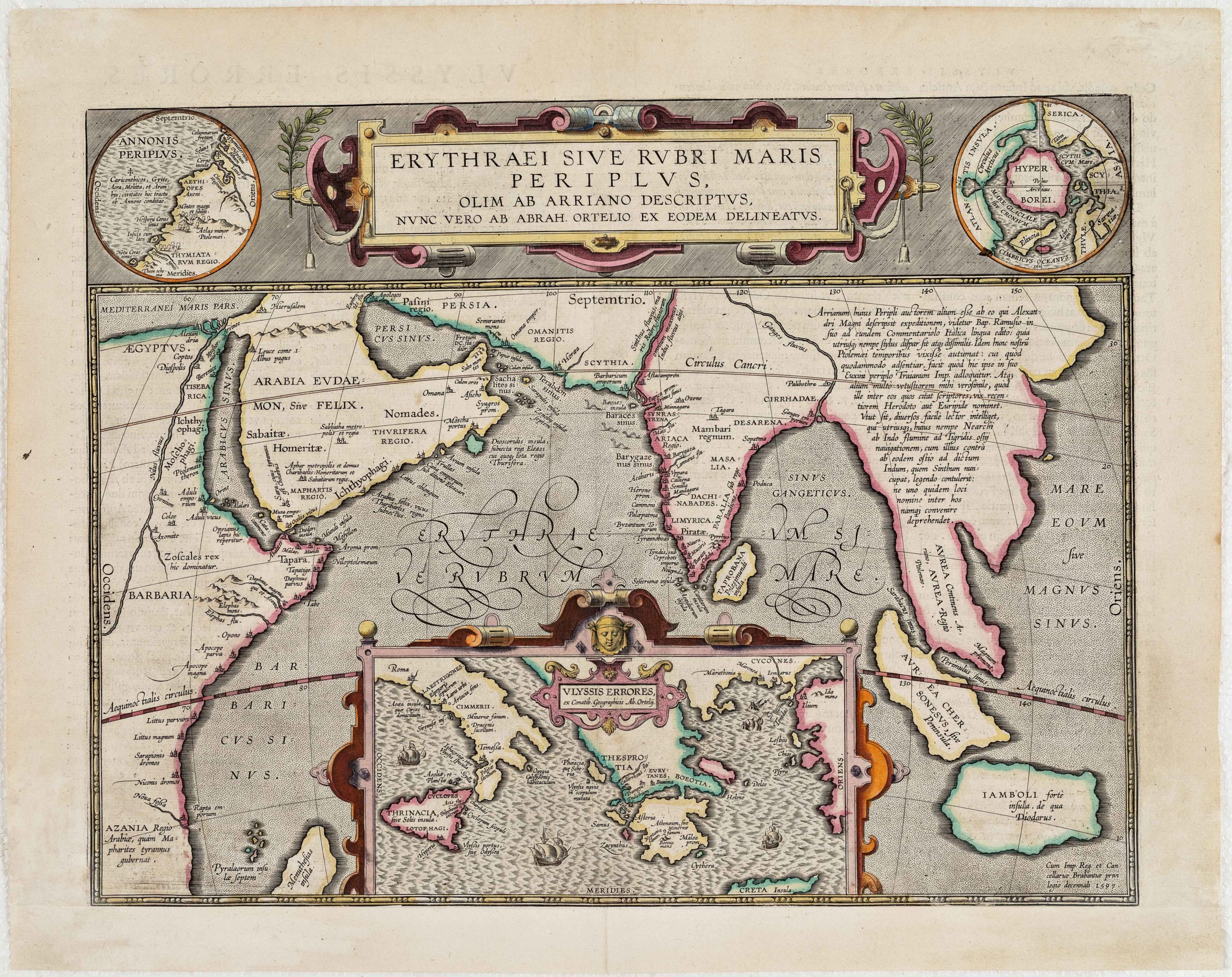
W. Blaeu’s decorative map of China.
Tartaria sive Magni Chami Imperium
Out of stock
Description
Blaeu’s map of Tartaria and northern China with information compiled by the English and Dutch explorers as well as the reports of Marco Polo and the Greek classics.
The title is symbolically engraved onto the saddle blanket of a camel, representing the trade over the Silk Road. Tiny devils and dragons frolic in the desert outside the Great Wall and numerous notes fill the unexplored regions.
Cartographer(s):
Willem Janszoon Blaeu (1571-1638) was one of the most important Dutch geographers and mapmakers of the 17th century. He was born the son of a herring merchant but traded fishmongering for studies in mathematics and astronomy. Blaeu’s first important breakthrough was winning an apprenticeship with the famous Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe. Working at Brahe’s Uranienborg observatory on the island of Hven, Blaeu learned various disciplines and technical skills. These included mathematics, astronomy, instrument-making, and more esoteric disciplines such as alchemy. Returning to his native Holland, Blaeu established a publishing business in Amsterdam. He sold instruments and globes, printed maps, and his own editions of some of the great philosophical works of contemporary intellectuals like Descartes and Hugo Grotius. Achieving notoriety as a cartographic pioneer, Blaeu was appointed Chief Hydrographer to the powerful Dutch East India Company, a position he held until he died in 1638.
When Willem died, his sons Cornelis (1610-1648) and Joan (1596-1673) took over the business. Joan had originally trained as a lawyer but never took up the practice, preferring to work on maps with his father. After Willem’s death, Joan continued publishing his father’s and his own maps. He also assumed his father’s position as a hydrographer for the Dutch East India Company. Towards the end of his life, Joan would dramatically expand his father’s Atlas Novus (1635), turning it into his own masterpiece, the Atlas Maior (1662-72).
When Willem died, his two sons Cornelis (1610-1648) and Joan (1596-1673) took over the business. Joan had originally trained as a lawyer, but never took up practice, preferring to work on maps with his father. After Willem’s death, Joan continued to publish both his father’s and his own maps. He also assumed his father’s position as hydrographer for the Dutch East India Company. Towards the end of his life, Joan would dramatically expand his father’s Atlas Novus (1635), turning it into his own masterpiece, the Atlas Maior (1662-72).
Condition Description
Light rubbing along centerfold with short marginal split and a few marginal chips; very good.
References
![[Pair of views] Rade et Ville de Sincapour & Rade de Sincapour prise de la maison du Gouverneur](https://neatlinemaps.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/NL-00896-harbor_Thumbnail-300x300.jpg)
![[Pair of views] Rade et Ville de Sincapour & Rade de Sincapour prise de la maison du Gouverneur](https://neatlinemaps.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/NL-00896-harbor_Thumbnail.jpg)