Ermete Pierotti (1820-1880) was the oldest of nine siblings in a family from Pontardeto in Pieve Fosciana (the family built the Palazzo Pierotti, which has served as the town hall since 1877). Pierotti worked as a military engineer in Genoa and later served as a captain in the Engineering Corps of the Sardinian King. In 1849, he was accused of desertion and the theft of 3596 lire from the troop’s treasury, which resulted in a dishonorable discharge from the army. Pierotti then traveled to Jerusalem and Egypt, where he worked as an engineer. In Egypt, he discovered the foundations of the Alexandria Library while laying the foundations for a Greek church, but it was in Jerusalem that he would put his surveying and engineering skills to work.
Pierotti arrived in Jerusalem in 1854 as a consultant for the Franciscan Order, which had custody of many of the Christian holy sites in the city. During his time there, Pierotti was involved in the restoration of the Crusader Era Church of St. Anne, located in the Old City near the Pool of Bethesda. Working with Ottoman engineer Assad Effendi, he later contributed to the restoration of the Qanat as-Sabil, the main aqueduct that supplied Jerusalem with water, which involved repairing the aqueduct’s channels and cisterns. Other building projects included work on the Temple Mount itself and the construction of both the Austrian Hospice and the so-called Alexanderhof (HQ of the Kaiserlichen Orthodoxen Palästina-Gesellschaft) in the Christian Quarter of the Old City. And finally, he helped design the road from Jaffa to Jerusalem, a significant engineering feat at the time.
Pierotti became interested in the city’s history and archeology during his time in Jerusalem. He conducted several excavations in the Old City. He discovered several important artifacts, including an inscription in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre that proved the existence of a church on the site during the Byzantine period. Pierotti’s work in Jerusalem earned him a reputation as a skilled engineer and pioneering archeologist. He became known for his attention to detail and ability to work under challenging conditions. In addition to his many projects, Pierotti’s legacy consists of publishing his magnum opus: Jerusalem Explored. A Description of the Ancient and Modern City (1864), which included an entire volume of lithographed plates based on Pierotti’s plans and converted photographs.
Despite his many successes, Pierotti’s work and position annoyed the British, who increasingly sought to establish a scientific presence in the Holy City, if not a colonial one. When competition arose between Pierotti and Captain Charles Wilson’s team of English Royal Engineers conducting the first Ordnance Survey of Jerusalem and surroundings in 1864, Pierotti’s reputation was deliberately tarnished by the disclosure of his criminal past, and for the rest of his life, he struggled to regain recognition for his achievements.
-
-
Add to cartQuick View
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
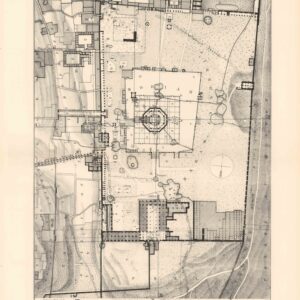
The Haram es-Sharif.
- $475
- A ground-breaking architectural plan of the Haram al-Sharif / Temple Mount.
-
Add to cart
-
-
Add to cartQuick View
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
Panorama of Jerusalem, seen from the Mount of Olives.
- $575
- A fantastic mid-19th-century panoramic view of Jerusalem.
-
Add to cart
-
-
Add to cartQuick View
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
Gate of Damascus.
- $300
- Jerusalem's famous Damascus Gate.
-
Add to cart
-
-
Add to cartQuick View
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
North-eastern view of Kubbet es-Sakharah, and of Kubbet es-Silsileh.
- $425
- The majestic Dome of the Rock.
-
Add to cart
-
-
Add to cartQuick View
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
Western View of el-Aksa, near the South-Western Angle.
- $320
- Lovely 19th-century view of al-Aqsa Mosque and surrounding countryside.
-
Add to cart
-
-
Add to cartQuick View
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
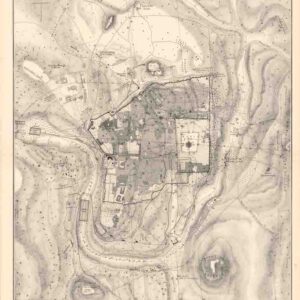
Plan of Ancient Jerusalem.
- $400
- Pierotti's scientific 19th-century plan depicting Ancient Jerusalem.
-
Add to cart
Archived
- Out of Stock
-
- Out of Stock
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
Gate of the entrance-door to the Church of the Resurrection.
- An evocative mid-19th century depiction of the famous entrance door to the Church of the Holy Sepulchre.
- Read moreQuick View
-
- Out of Stock
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
Pool of Mamillah, or Serpent’s Pool (according to Josephus), near the Monument of Herod on the west of the city.
- An ancient Jerusalem reservoir.
- Read moreQuick View
-
- Out of Stock
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
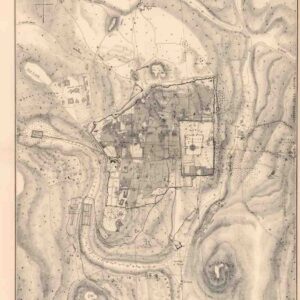
Plan of Modern Jerusalem.
- 1864 city plan of Jerusalem.
- Read moreQuick View
-
- Out of Stock
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
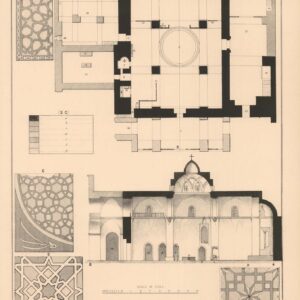
Plans and sections of the Armenian Church of S. James, and mosaics.
- 19th-century architectural plan of the Armenian Church of Saint James.
- Read moreQuick View
-
- Out of Stock
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
View of the arch of the Ecce Homo, with the smaller arch to the north, discovered by Pierotti.
- Depiction of a discovery.
- Read moreQuick View
-
- Out of Stock
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
Eastern View of the Golden Gate.
- 19th-century view of Jerusalem's Golden Gate.
- Read moreQuick View
-
- Out of Stock
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
Wailing Place of the Jews, A Portion of the Ancient Wall…
- Pierotti's evocative 19th-century view of the Wailing Wall.
- Read moreQuick View
-
- Out of Stock
- Eastern Mediterranean - Holy Land
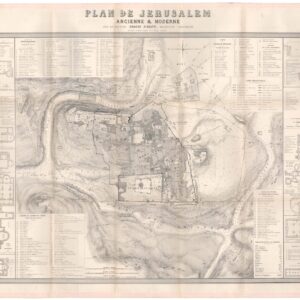
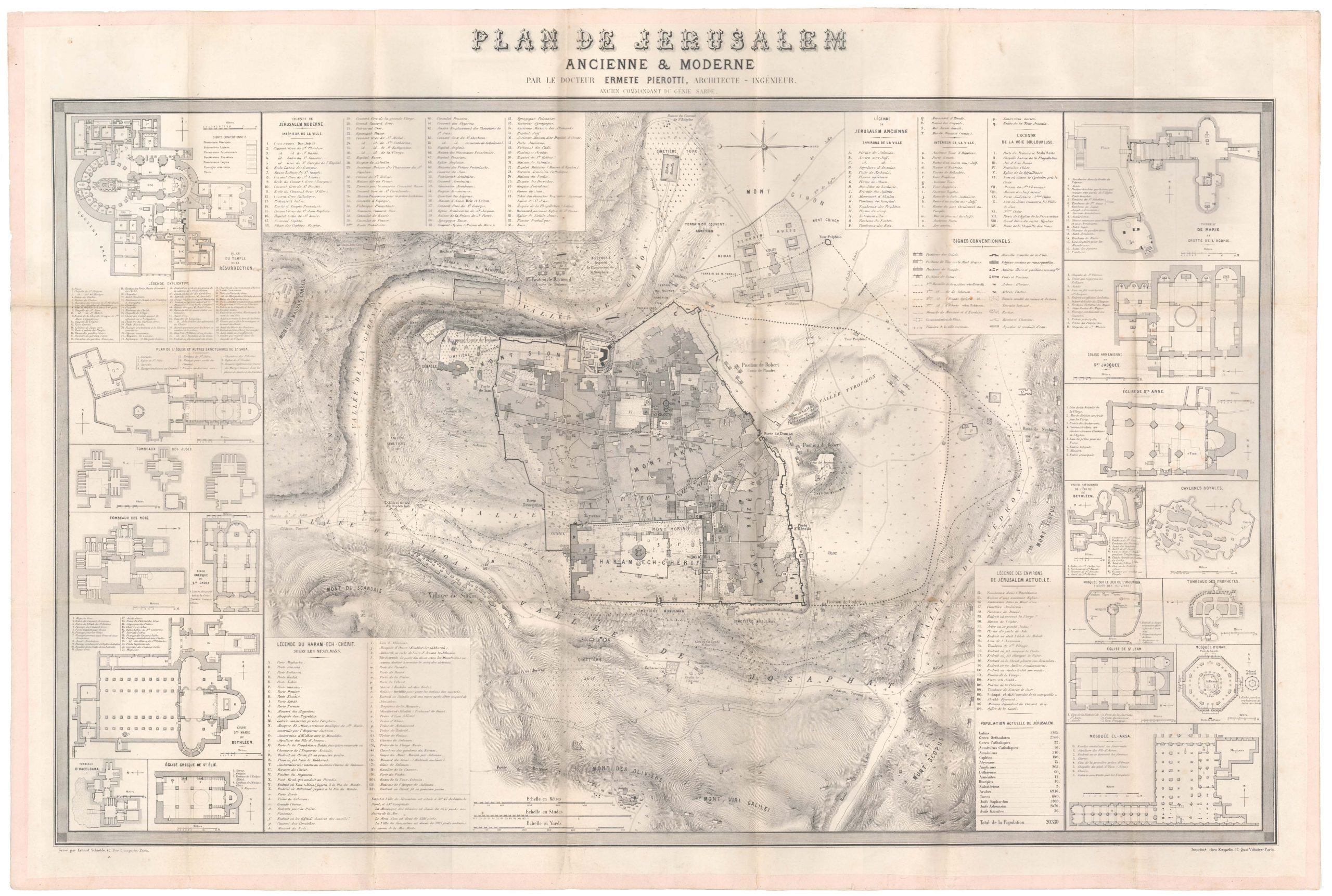
Plan De Jerusalem Ancienne & Moderne
- Plan of the Old City of Jerusalem by the Ottoman city’s official architect and engineer.
- Read moreQuick View
-